For automobile manufacturers and suppliers, hot forming of sheet metal is particularly important. It is applicable to all quality grades of steel. The components produced using this method are lighter in weight and have higher collision test values.
Hot forming is a sheet metal forming process, also known as hot stamping or stamping hardening. All forming processes must be above the recrystallization temperature of the metal used. During the hot forming process of sheet metal, the material will recover and soften. In this way, although the forming force is low, the equivalent effect becomes very high. Hot forming includes several processes such as forging, hot rolling, and extrusion. The forming technology complies with DIN 8582 standard, and even high-strength materials can be processed according to requirements. This process is particularly suitable for components that must withstand high loads (cylinders, crankshafts, connecting rods, gears).
In warm forming, the temperature used is between the temperature range of cold forming and hot forming of sheet metal. Industrial users combine the advantages of both methods and try to avoid the disadvantages of both technologies by selecting specific forming temperatures. Compared to cold forming, warm forming requires less forming force. Compared to hot formed components, cooling components have smaller dimensional tolerances.
During the cold forming process, the forming temperature is lower than the recrystallization temperature. To achieve equivalent strain, higher forming force is required. The precision components produced in this way have small dimensional tolerances and good surface structures. To achieve solidification of the formed workpiece, recrystallization annealing treatment is required.
Sheet metal forming in the form of hot forming is higher than the recrystallization temperature. This is the temperature at which metal undergoes 100% recrystallization during the forming process. The recrystallization temperature is 40% or 50% of the absolute melting temperature. At these temperatures, dislocations in the microstructure will be eliminated: new grains will be generated, and the hardness of the material will decrease. The expansion of materials during hot forming can be visually displayed through flow curves. It represents the relationship between the yield stress and the corresponding equivalent strain during the hot forming process. The yield stress itself is influenced by the working temperature and forming speed.
For example, hot forming during deep drawing is carried out through direct or indirect hot forming of sheet metal. In the direct hot forming process, before the first forming process, the material is heated in an oven to above the recrystallization temperature. Then put the material into the press and deep drawing tool. After plastic forming, the material is cooled in a closed mold that has been cooled. The typical method of indirect hot forming is to heat after the first forming process, then directly perform the final stretching, and rapidly cool during the pressing process. Boron alloy steel 22MnB5 is commonly used for hot formed sheet metal. By transforming austenite into martensite, excellent material properties can be achieved.
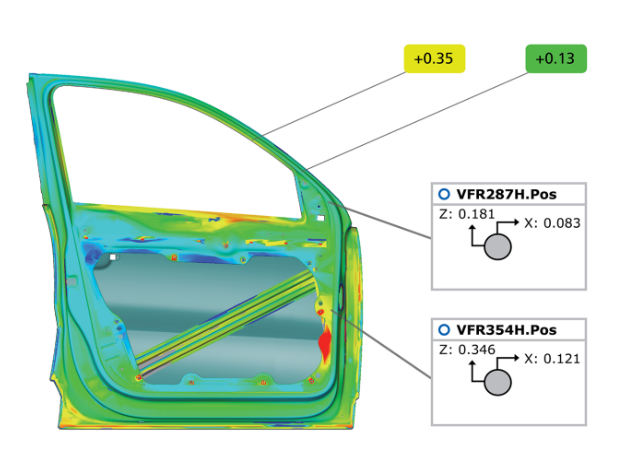
Recently, car manufacturers have favored this forming technology. The reason is that components manufactured using this technology have higher collision safety. In addition, hot forming and cooling special steel can also reduce vehicle weight. Using this technology, car manufacturers can produce side beams, door reinforcements, door sills, roof frames, roof racks, bumper supports, as well as A-pillars and B-pillars.
To prevent hot formed steel from scaling in the furnace, these steels are coated with a special layer of aluminum silicon coating. In order to maintain stable high-quality production, all components must go through a quality assurance process. This process is automatically completed through optical measurement technology.
Advantages:
The material does not solidify and has good formability
Low rebound
Can create more complex shapes
Low residual stress and good dimensional stability
Thinner wall thickness and lighter components
Only a small forming force is required
Suitable for all steel materials
Disadvantage:
Due to the high working temperature, there are slight scales on the surface
In extreme cases, components may warp
Larger dimensional tolerance
Melting furnaces result in high energy costs
Forming a flying edge
Looking for a trusted China sheet metal forming factory? HSJ combines advanced hot forming technology with years of expertise to deliver durable, high-performance components. From design to production, we ensure every project benefits from precision, cost-effectiveness, and reliable service. Discover how HSJ can support your business success.